The Role of IT in Business Success: Why Every Company Needs a Strategy
Introduction
In today’s digital age, technology is at the core of business success. Whether you’re a startup or a well-established company, IT plays a crucial role in enhancing productivity, streamlining operations, and driving growth. However, many businesses overlook the need for a structured IT strategy, leading to inefficiencies, security risks, and missed opportunities.
In this article, we’ll explore why every company needs an IT strategy and how it contributes to overall business success.
1. Enhancing Operational Efficiency
A well-planned IT strategy enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks to minimize human errors, increase accuracy, and save valuable time, optimizing workflows through the integration of advanced software and AI-driven systems that streamline operations, and leveraging cloud-based solutions to facilitate seamless remote work, real-time data access, and collaboration across multiple locations. Additionally, businesses can implement data synchronization tools to ensure consistency across departments, cybersecurity measures to protect critical systems from disruptions, and scalable IT infrastructures that support business growth. A prime example is companies utilizing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, which not only integrate sales, finance, and inventory management but also provide real-time analytics, improve supply chain visibility, and enhance decision-making, ultimately reducing redundancies and maximizing productivity.
2. Improving Customer Experience.

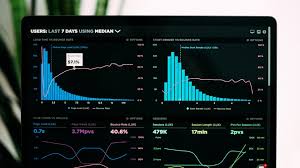
3. Enabling Data-Driven Decision Making.

4. Supporting Scalability & Future Growth.
As businesses expand, their IT requirements become more complex, making a well-structured IT strategy essential for scalability by implementing cloud-based solutions that offer flexible storage, computing power, and remote accessibility to accommodate growth; investing in modular IT infrastructure that allows seamless expansion without overhauling existing systems, ensuring cost-effective upgrades; and adopting flexible software solutions capable of integrating with new tools, third-party applications, and evolving technologies to enhance operational efficiency, as demonstrated by companies like Uber and Airbnb, which successfully scaled by leveraging IT strategies that could support rapid user growth, high transaction volumes, and global operational demands.

Conclusion


